Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivation Explained in 2023
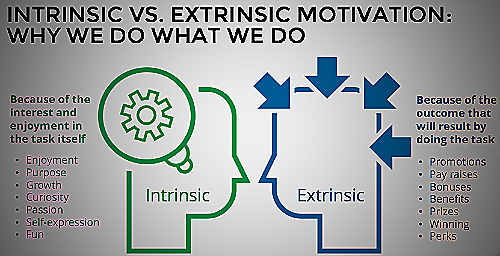
Extrinsic and intrinsic motivation are two types of motivation that play a crucial role in personal and professional growth. Intrinsic motivation is driven by internal factors, such as personal satisfaction, enjoyment, and fulfillment.
On the other hand, extrinsic motivation comes from external factors, such as rewards, recognition, and career advancement. Understanding the difference between the two is important for achieving success in both personal and professional goals.
Check out this Youtube video on “Extrinsic vs Intrinsic Motivation” to understand how to motivate employees beyond just money and rewards.
What Is Extrinsic Motivation?
Extrinsic motivation refers to any external factors that drive behavior and performance. This type of motivation comes from rewards or punishments that result from performing a certain behavior or achieving a particular outcome.
In the workplace, extrinsic motivation can come in the form of bonuses, promotions, or recognition from peers. Outside of work, extrinsic motivation can be seen when people exercise to lose weight or receive praise for completing a task.
Extrinsic motivation can be a powerful way to create short-term results, but it tends to lose its effectiveness over time as individuals become less interested in the reward or the reward loses its value. Furthermore, excessive extrinsic rewards can actually decrease intrinsic motivation and creativity.

What Is Intrinsic Motivation?
Intrinsic motivation refers to behavior that is driven by internal rewards. It involves engaging in an activity simply because you find it enjoyable or satisfying.
In other words, intrinsic motivation comes from within. There is no external reward or pressure, and the behavior is its own reward.
Examples of intrinsic motivation include doing a hobby, exercising, taking on a challenging project at work, or learning something new just for the sake of learning.
Research has found that intrinsic motivation can lead to better performance, engagement, and satisfaction in both personal and professional settings. When individuals are intrinsically motivated, they are more likely to put in effort and persistence, and feel a sense of personal autonomy and competence in their work.

Extrinsic vs. Intrinsic Motivation: Which Is Best?
When it comes to motivation, there are two basic types: extrinsic and intrinsic. Extrinsic motivation refers to external factors, such as rewards or punishments, that drive us to perform a specific behavior or engage in an activity.
In contrast, intrinsic motivation comes from within and arises when we feel a personal satisfaction or enjoyment from doing something.
Comparing extrinsic and intrinsic motivation
Extrinsic motivation can be useful in certain situations, such as when we need to perform a task that is not inherently enjoyable or when we need to meet a specific goal. For example, a student may study hard for an exam in order to earn a good grade and please their parents or teacher, even if they do not find the material particularly interesting.
On the other hand, intrinsic motivation is often more effective in the long term and leads to greater satisfaction and fulfillment. When we are intrinsically motivated, we are engaged in an activity because we find it inherently enjoyable or satisfying.
For example, an artist may spend hours painting because they love the process of creating something beautiful, even if they do not receive any external rewards for their work.
Pros and cons of each type of motivation
Extrinsic motivation can be effective in the short term and can help us achieve specific goals, but relying too heavily on external rewards can eventually lead to burnout and decreased motivation. When we are motivated primarily by external factors, we may begin to feel like we are working purely for the reward and lose sight of the intrinsic satisfaction that comes from completing a task or achieving a goal.
On the other hand, intrinsic motivation can be highly effective over the long term. When we are intrinsically motivated, we are more likely to stick with an activity or task even if we encounter obstacles or setbacks, because we are motivated by the inherent satisfaction we get from the process of engaging in that activity.
Intrinsic motivation is also associated with greater satisfaction and well-being overall, as we feel a sense of accomplishment and pride in the work we are doing.
How to balance and integrate extrinsic and intrinsic motivation for optimal performance and satisfaction
In order to achieve optimal performance and satisfaction, it is important to find a balance between extrinsic and intrinsic motivation. This might involve finding ways to integrate external rewards or goals with the inherent satisfaction that comes from the activity or task itself.
For example, a runner may train for a race in order to achieve a specific goal, but also find joy in the process of running and pushing themselves to be their best.
Ultimately, the key is to recognize the value of both types of motivation and find ways to use them effectively in different situations. By integrating intrinsic and extrinsic motivation, we can achieve our goals, perform at our best, and feel satisfied and fulfilled in the process.
When to Use Extrinsic Motivation
Extrinsic motivation is the type of motivation where we are motivated to perform a behavior or engage in an activity because we want to earn a reward or avoid punishment. It is helpful in situations where our internal motivation is not enough to get us going.
In extrinsic motivation, external factors such as monetary rewards, recognition, or gifts become the driving force behind our actions. It can be useful in some situations such as meeting work deadlines, completing a challenging task, or achieving a specific goal.
Identifying Extrinsic Motivated Behavior
Extrinsic motivated behavior can be identified by the presence of external factors influencing the individual to perform an action. It can be seen as individuals displaying behavior that they would not normally exhibit under normal circumstances.
Signs of extrinsic motivated behavior include individuals working towards a goal to gain a reward or recognition, doing a task because of pressure from peers or bosses, or completing a task to avoid punishment.
Using Extrinsic Motivation to Achieve Personal and Professional Goals
Although intrinsic motivation is usually considered to be a more effective form of motivation, extrinsic motivation can also be effective in achieving personal and professional goals. It is important to note that extrinsic motivation should only be used as a supplement in situations where intrinsic motivation is not enough.
When using extrinsic motivation, the key is to ensure that the rewards are meaningful to the individual and not seen as a mere token gesture. The reward can be financial, recognition, promotion, or other tangible benefits that the individual values.
By offering suitable rewards, an employer or individual can incentivize behaviors that can help them achieve their goals.
In conclusion, extrinsic motivation is a useful tool in situations where intrinsic motivation is not enough to get the desired results. However, it should be used wisely and only as a supplement to intrinsic motivation.
By offering suitable rewards, an employer or individual can incentivize the desired behavior and ultimately achieve their goals.
How Do Intrinsic Motivation and Extrinsic Motivation Influence Learning?
The role of extrinsic and intrinsic motivation in learning is crucial in understanding the different factors that drive students to engage in academic or work-related tasks. Intrinsic motivation comes from within, where individuals engage in an activity because they enjoy it and get personal satisfaction from doing it.
In contrast, extrinsic motivation arises from external factors, where individuals do something to gain an external reward.
Research shows that intrinsic motivation is typically more effective long term for completing tasks and achieving goals in a way that makes individuals feel fulfilled. On the other hand, while extrinsic motivation is helpful in certain situations, it may eventually lead to burnout or lose its effectiveness over time.
It is essential to have a balance of both types of motivation in learning and development.
How to Foster Intrinsic Motivation in the Classroom and Workplace
Fostering intrinsic motivation in the classroom and workplace can enhance engagement, creativity, and problem-solving skills. Here are some strategies to promote intrinsic motivation:
- Offer choices: Students and employees are more motivated when they feel they have a choice in what they are doing. Providing choices can enhance feelings of ownership over tasks and increase motivation.
- Encourage mastery-oriented goals: Setting and achieving achievable mastery goals fosters intrinsic motivation. The focus shifts from being motivated by grades or rewards to being motivated by learning and developing skills.
- Provide feedback: Giving constructive feedback can enhance intrinsic motivation by increasing feelings of competence and self-efficacy. Feedback should be related to skill development and provide actionable steps for improvement.
- Encourage autonomy and competence: Encouraging autonomy and competence can foster intrinsic motivation. Allowing students or employees to take ownership of their work and providing opportunities for skill development can increase motivation.
Strategies to Incorporate Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivation in Learning and Development
While intrinsic motivation is typically more effective long term, extrinsic motivation can also play a role in learning and development. Here are some strategies to incorporate both types of motivation:
- Use rewards strategically: While rewards can be beneficial, they should not be the sole source of motivation. Using rewards to reinforce behavior and promote intrinsic motivation can be beneficial.
- Set goals: Setting goals can motivate both intrinsically and extrinsically. Goals should be challenging and achievable, promoting feelings of accomplishment and progress.
- Provide recognition: Recognition for a job well done can foster intrinsic motivation by increasing feelings of competence and mastery. Public recognition can be extrinsically motivating, but should also promote a sense of accomplishment.
- Create a supportive environment: Creating a supportive environment can foster intrinsic motivation. Supportive environments can increase feelings of competence, autonomy, relatedness, and usefulness, promoting intrinsic motivation.
In conclusion, understanding the role of extrinsic and intrinsic motivation in learning and development is essential in supporting students and employees. Intrinsic motivation supports seeking knowledge for its own sake, while extrinsic motivation helps individuals become driven and competitive.
Establishing a balance between both types of motivation can enhance engagement, creativity, and problem-solving skills while increasing motivation and feelings of accomplishment.
Examples of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic motivation is self-driven. This type of motivation comes from within and is based on personal satisfaction and enjoyment.
Here are some examples of daily activities that generate intrinsic motivation:
- Reading a book purely for pleasure
- Enjoying a sport because it is fun and challenging
- Participating in a volunteer activity because it aligns with personal values and beliefs
- Completing a puzzle or task because of the feeling of accomplishment it brings
In order to use intrinsic motivation to achieve long-term goals, it is important to find value and purpose in the task at hand. By doing so, one can establish a sense of personal achievement and fulfillment, which becomes the motivating factor.
Extrinsic Motivation
Unlike intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation is driven by external sources. This type of motivation is based on rewards, recognition, and fear of punishment.
Examples of daily activities and workplace situations that generate extrinsic motivation include:
- Working overtime for additional pay
- Meeting a deadline to receive a bonus
- Participating in a sales contest to earn a prize
- Completing a task to avoid disciplinary action
Extrinsic motivation can be used to achieve short-term goals, but it may lead to burnout or lose its effectiveness over time. To strengthen extrinsic motivation, it is important to align the rewards and recognition with personal values and goals.
This will increase motivation and satisfaction in the long term.
How to Leverage Extrinsic Motivation at Work
Extrinsic motivation is a crucial aspect when it comes to improving work performance and productivity. It is the external reinforcement that drives individuals to behave in a certain way.
Here are some ways to leverage extrinsic motivation at work:
Set Goals and Rewards
Setting specific goals helps employees understand what is expected of them and motivates them to work towards achieving those goals. Pairing these goals with rewards makes the employees more engaged in their tasks and encourages them to work harder towards achieving the goals.
Offer Incentives
Incentives like bonuses, promotions, and public recognition incentivizes employees to work harder. Knowing that their hard work is being appreciated and rewarded keeps them motivated and focused on achieving their goals.
Fostering Healthy Competition
Create an environment that encourages competition between employees. This helps establish individual goals and encourages employees to push themselves beyond their limits.
Provide Opportunities for Growth
Offering training, development, and career advancement opportunities is a powerful way to incentivize employees to work harder. Providing employees with a clear path towards career growth and development is a great way to leverage extrinsic motivation at the workplace.
Encourage Collaboration
Encouraging teamwork and collaboration helps create a positive work environment. Team members working together towards a common goal keeps them motivated and invested in their work.
Overall, leveraging extrinsic motivation is an effective way to improve work performance. While extrinsic rewards and recognition incentivizes employees to work harder, it should not be the only motivating factor.
A healthy combination of both, extrinsic and intrinsic motivation, helps develop engaged employees who are invested in their work and achieve their goals.
How to Leverage Intrinsic Motivation at Work
In order to nurture intrinsic motivation at work, it is important to create an environment that fosters growth, autonomy, and creativity. One way to facilitate this is by providing employees with opportunities to learn and develop new skills, as well as encouraging them to take on new challenges and responsibilities.
Another key factor in fostering intrinsic motivation is to align personal and organizational values. This means highlighting the core values of the company in a way that resonates with employees on a personal level, making it clear that their individual contributions are essential to the overall success of the organization.
At the same time, it is important to recognize the limits of intrinsic motivation, and to offer extrinsic rewards when appropriate in order to maintain performance and satisfaction. For example, recognizing and rewarding exceptional performance can help incentivize employees to continue to improve and strive for excellence.
In order to leverage intrinsic motivation in the workplace, it is important to strike a balance between creating an environment that fosters growth and autonomy, aligning personal and organizational values, and recognizing and rewarding exceptional performance when appropriate.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is intrinsic motivation?
What is extrinsic motivation?
What are some examples of intrinsic motivation?
What are some examples of extrinsic motivation?
Which type of motivation is more effective long-term?
Conclusion
Extrinsic and intrinsic motivation are two important factors that can influence a person’s behavior, whether in the workplace or in personal life. While extrinsic motivation can be helpful in certain situations, it may eventually lead to burnout or lose its effectiveness over time.
On the other hand, intrinsic motivation is typically more effective long term for completing tasks and achieving goals in a way that makes you feel fulfilled. A balance between the two can help individuals develop good study habits, an investment in learning, and a sense of personal satisfaction and accomplishment.
When it comes to motivation, there are two types: extrinsic and intrinsic. Extrinsic motivation comes from external rewards such as bonuses, promotions, or recognition, while intrinsic motivation comes from within and is driven by personal satisfaction and a sense of fulfillment.
While extrinsic motivation can be effective in driving short-term performance, it may eventually lead to burnout and disengagement. In contrast, intrinsic motivation is more likely to foster employee engagement and job satisfaction in the long term.

