Information Processing Theory 2023: The Ultimate Guide
Information Processing Theory (IPT) is a cognitive approach that explains how our brain processes, stores, and retrieves information from the environment. In finance, understanding IPT can help individuals manage financial information effectively and make informed decisions.
Attention
The first stage of IPT is attention, where people selectively focus their attention on relevant stimuli while filtering out distractions. In finance, it is essential to pay attention to critical financial information such as market trends, interest rates, and financial news to make informed investment and financial decisions.
Sensory Memory
Sensory memory is the second stage of IPT, where the brain temporarily stores sensory information from the environment. In finance, sensory memory helps individuals recognize financial stimuli such as financial statements, graphs, and charts.
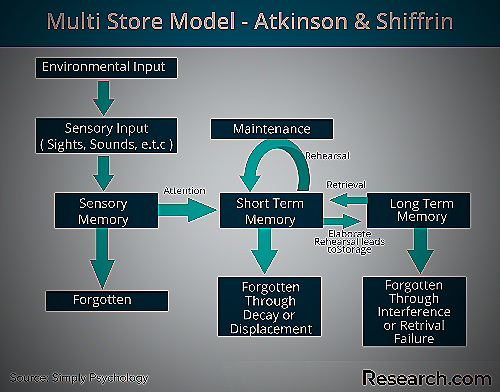
Short-term Memory
The third stage of IPT is short-term memory, where the brain stores information for a short time to process it actively. In finance, short-term memory helps individuals remember financial details like account balances, interest rates, and loan payments.
Check out this informative Youtube video on “Information Processing Theory Explained” to better understand how our brain processes and interprets external stimuli, which can be applied to various fields including employee engagement and remote work!
History of Information Processing Theory
Information Processing Theory (IPT) is a psychological framework that explains how humans acquire, store, and retrieve information. It originated during the 1950s, when computers began to gain prominence, and psychologists were inspired by the idea of using computers as a model for understanding human cognition.
George Armitage Miller, one of the founders of cognitive psychology, introduced the theory of IPT in a paper titled “The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two: Some Limits on Our Capacity for Processing Information.”
The theory was a response to behaviorism, which dominated psychology at the time. Behaviorists only studied observable behaviors, which led some psychologists to dub the mind as an unknowable “black box.”
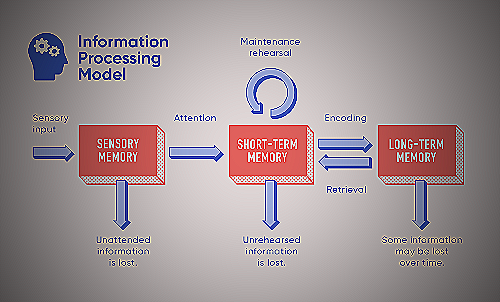
As a result, cognitive psychologists turned to IPT to understand how the mind processes information. IPT posits that humans perceive information, encode it into memory, retrieve it, and manipulate it using mental processes such as attention, perception, and memory.
These processes help individuals function in their environment by making sense of and responding to incoming sensory information.
Since its inception, IPT has undergone significant development and refinement. It has been applied across disciplines, including education, computer science, and clinical psychology.
IPT has also been used to develop educational theories and programs that facilitate learning. It has made it possible for psychologists to investigate the complexity of the human mind and has opened up new ways to study cognitive processes, such as neuroscience and neuroimaging.
Basic Assumptions of Information Processing Theory
Information Processing Theory posits that the human mind works similarly to a computer, capable of receiving, storing, and processing information. The theory assumes that cognitive processes take place in a series of stages, during which the mind receives, encodes, stores, and retrieves information.
These stages involve attention, perception, memory, and retrieval. Information Processing Theory suggests that information is processed and stored in the brain through the use of sensory registers, working memory, and long-term memory.
The theory also proposes that cognition involves the manipulation and transformation of information in systematic ways. These processing systems work together to transform or alter information to make it more meaningful and useful.
In this way, information processing in humans resembles that in computers, with the mind serving as the processor of information.
Models of Information Processing Theory for Finance
The Conceptual Model of Financial Information Processing
The Conceptual Model of Financial Information Processing explains how people interpret financial information and make decisions based on that interpretation. The model consists of four stages: attending, encoding, storing, and retrieving.
In the attending stage, individuals focus their attention on relevant financial information. Next, the encoding stage involves translating that information into a mental representation.
In the storing stage, individuals store the mental representation in their long-term memory. Lastly, the retrieving stage involves accessing the stored information to make financial decisions.
This model is beneficial in finance as it helps individuals make better decisions based on a systematic approach to processing financial information.
The Competing Risks Model
The Competing Risks Model is a statistical model that can be used in finance to predict and manage financial risks. The model is based on the concept that there are multiple risks competing against each other in the financial market.
These risks can be classified into different categories, such as systematic and unsystematic risks. The model analyzes the interactions between these risks and estimates the probability of various outcomes.
This model is useful in finance as it enables investors and financial managers to make sound decisions by identifying the major risks and taking appropriate actions to mitigate them.
How Information Processing Theory Aids in Financial Decision Making
Financial decisions are complex and require consideration of various factors. To make better decisions, it is essential to understand how individuals process information and how it affects decision-making processes.
According to the information processing theory, individuals record, store, and retrieve information in stages that affect how they make financial decisions.
Encoding Information
Encoding information is the first step of the information processing model. It involves paying attention to the relevant information and categorizing it to store it in memory.
When making financial decisions, individuals need to encode information such as market trends, investment risks, and financial implications of decisions.
Storage and Retrieval
Information that is encoded is stored in memory and can be retrieved when making financial decisions. Memory storage has a limited capacity, and not all information can be stored in long-term memory.
The information processing theory suggests that individuals use different strategies to store and retrieve information when making decisions.
In financial decision-making processes, individuals need to retrieve relevant and accurate information from their memory. The process involves searching for and recalling previously encoded information to analyze and evaluate the financial implications of the decision.
Working Memory
Working memory is the part of memory where individuals consciously process and manipulate information. It is crucial in financial decision-making processes as it determines how well individuals can make use of the information available.
The information processing theory proposes that individuals’ working memory capacity can affect their decision-making processes. Those with larger working memory capacities can process more information and make better-informed financial decisions.
The information processing theory provides insight into how individuals encode, store, and retrieve information, and how working memory affects decision-making processes. Understanding the role of the information processing theory in financial decision-making can help individuals make better decisions by improving their information processing abilities and capacity.
Limitations of Information Processing Theory in Finance
The information processing theory has limitations in finance, and it is essential to understand them.
One limitation of Information Processing Theory in finance is that individuals’ cognitive processing cannot be accurately predicted. Humans can make errors in judgment when making financial decisions, and this can adversely affect their decision-making.
Another limitation is that not all financial decisions can be explained by the information processing theory. The theory focuses on cognitive mechanisms and does not account for other factors such as emotions, intuition, and social influence that can affect financial decision making.
Also, studies have shown that people’s cognitive abilities decline with age, which can affect their ability to process financial information and make decisions. This means that the information processing theory may not accurately describe older adults’ financial decision-making processes.
Applications of Information Processing Theory in Finance
Financial Planning
Information Processing Theory can aid in developing effective financial plans for long-term success by breaking down the process into stages where individuals attend to, encode, store, and retrieve information. By understanding how individuals process information, financial planners can tailor their communication and strategies to better match their clients’ cognitive processes.
Additionally, breaking down financial plans into smaller, more manageable steps can help individuals process the information more effectively.
Risk Management
Information Processing Theory can also benefit risk management in finance. By understanding how individuals process and evaluate risks, financial professionals can better communicate the potential hazards and potential gains associated with various investment decisions.
This can lead to more informed and effective decision making by individuals and organizations alike.
Conclusion
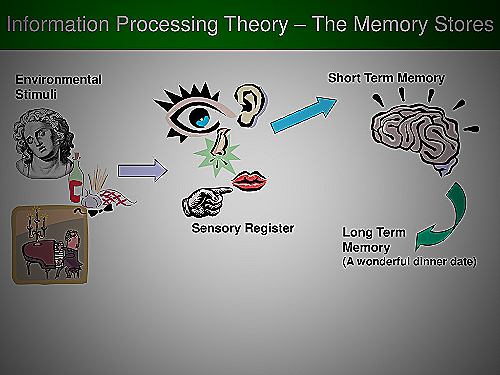
Information processing theory is a cognitive theory that focuses on how information is recorded, stored, and retrieved in the brain. It is based on the idea that humans do not merely react to their environment but also process the information they receive.
The theory describes how the brain filters information through four stages: attending, encoding, storing, and retrieving. It also explains how long-term memories are encoded and stored in the brain.
Understanding how information is processed can have significant implications for finance, including improving decision-making, risk management, and forecasting. The use of cognitive-based technology, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, is making significant inroads into finance as it enables quicker and better-informed decision-making.
Although theorists of information processing differ from other cognitive theories, such as Piagetian thinking, they assert that intellectual development results from both nature and nurture—that is, from biological factors as well as environmental experiences.
References
- Information Processing
- What Is Information Processing Theory?
- Information Processing Theory
- Understanding Information Processing Function

