Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation Examples (2023)
Overview of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation
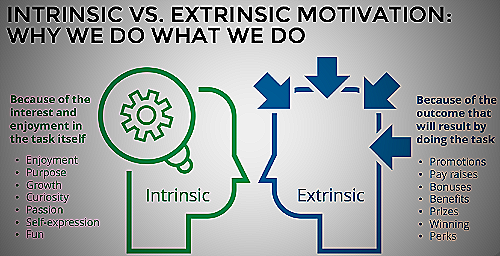
Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation are two different types of motivation that drive individuals to act in certain ways. Intrinsic motivation comes from an individual’s internal desire to do something simply for the enjoyment and personal satisfaction it brings.
On the other hand, extrinsic motivation arises from external factors such as rewards, recognition, and other benefits. Understanding the difference between these two types of motivation can be helpful for individuals in reaching their goals and achieving success in their personal and professional lives.
In this article, we will explore some examples of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation and how they play a role in motivating individuals.
Looking for practical examples of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation? Check out this Youtube video on “Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Motivation Explained”.
It provides valuable insights and practical tips for enhancing both types of motivation in your personal and professional life.
If you want to boost your productivity, engagement, and satisfaction at work, you can’t miss this Youtube video on “Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Motivation Explained”. It’s a must-watch for anyone who wants to harness the power of motivation in their career and personal development.
Intrinsic Motivation Examples
Definition of intrinsic motivation
Intrinsic motivation is the type of motivation that originates from internal factors, such as personal interests or enjoyment of a task, rather than an external reward.
Examples of intrinsic motivation in the workplace
Employees who are intrinsically motivated tend to be more engaged and productive. Examples of intrinsic motivation in the workplace include an employee who is passionate about their work and loves their job, someone who enjoys the challenge of their work, and employees who take pride in their work and the quality of their output.
Examples of intrinsic motivation in personal life
Examples of intrinsic motivation in personal life include hobbies, sports and artistic pursuits. These activities are carried out because they bring personal satisfaction and a sense of fulfillment, rather than external rewards.
For example, someone who loves painting will paint for the pleasure and joy of creating art, regardless of whether or not they earn money from their work. Similarly, someone who runs marathons does so because of the sense of accomplishment and enjoyment they get from running, not because they expect to win prizes or gain external recognition.
Scientific studies on the benefits of intrinsic motivation
There have been numerous studies on the benefits of intrinsic motivation. Intrinsically motivated individuals are often found to be more satisfied with their work and experience less stress.
They are also more likely to take on new challenges and persevere through difficult tasks. One study found that intrinsic motivation is positively linked to creativity and innovative thinking.
Extrinsic Motivation Examples
Definition of extrinsic motivation
Extrinsic motivation refers to engaging in an activity to receive external rewards or avoid punishments. It involves performing an action to achieve external goals, such as earning money, gaining recognition, or pleasing others.
Instead of deriving satisfaction from the activity itself, individuals obtain satisfaction from the rewards or consequences that come with it.
Examples of extrinsic motivation in the workplace
In the workplace, extrinsic motivation can take the form of bonuses, promotions, public recognition, or other incentives. For instance, an employee may work overtime to earn more pay, or an individual may take on an undesirable task to impress their boss.
The promise of a raise or promotion may encourage employees to work harder and achieve better results, even if they do not enjoy the work itself. These extrinsic rewards can help boost performance and productivity, but they may also lead to burnout or disengagement if they are the sole motivator for an individual.
Examples of extrinsic motivation in personal life
Extrinsic motivation can also play a role in personal life, where external rewards like money, status, or social recognition serve as the motivators. For example, an individual may exercise to achieve a more attractive physique or receive compliments from others, rather than for the intrinsic rewards of feeling healthier and stronger.
Likewise, students may study hard to achieve high grades and earn scholarships, rather than because they enjoy the subject matter. These external factors can drive an individual to excel in specific areas, but they may also lead to feelings of emptiness or dissatisfaction if the rewards do not align with their personal values or goals.
Scientific studies on the benefits and limitations of extrinsic motivation
Research has shown both benefits and limitations of extrinsic motivation. Some studies suggest that extrinsic rewards can increase performance and productivity in the short term, but they may lead to burnout or a decrease in job satisfaction in the long run.
On the other hand, other studies suggest that intrinsic rewards, such as autonomy and a sense of purpose, lead to higher job satisfaction, engagement, and creativity.
Comparing Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation are two different types of motivation that are often discussed in psychology. Understanding the differences between the two can help individuals better understand their own driving forces and achieve their goals.
Key differences between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation
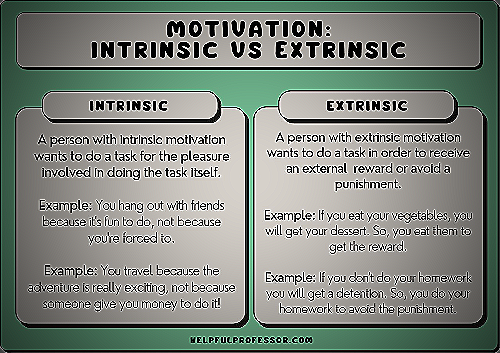
Intrinsic motivation comes from within, and it is propelled by the inherent satisfaction and enjoyment one experiences from the activity itself. Extrinsic motivation, on the other hand, is prompted by an external reward or pressure to perform.
One notable difference between these two types of motivation is how much control one feels over the circumstances that motivate them. Intrinsic motivation puts the individual in control, thus fostering a sense of self-determination, a feeling of autonomy, and a stronger sense of their own abilities.
However, extrinsic motivation can sometimes strip individuals of their sense of autonomy, leading them to believe that their motivations are not their own and that they have little to no control over the outcome.
Examples of situations where intrinsic motivation is preferable
Intrinsic motivation can be highly beneficial, as it is often associated with creative problem solving, personal growth, and an increased sense of well-being. Activities like writing, creating artwork, or playing instruments can be driven by intrinsic motivation, as individuals often report feeling a sense of flow and enjoyment when performing these tasks.
Examples of situations where extrinsic motivation is preferable
While intrinsic motivation is often desirable, there are many situations where extrinsic motivation can be useful, especially in a work setting. For example, a deadline or the promise of a bonus can motivate an employee to complete a task on time or even go above and beyond in their work.
Additionally, external rewards can sometimes lead to feelings of accomplishment and success, which can in turn boost intrinsic motivation.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation can help individuals better assess what drives them and how they can best leverage these motivations to achieve their goals and desires. By focusing on the right type of motivation for each situation, individuals can create a more fulfilling and engaging life for themselves.
How to Use Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation to Achieve Goals
One of the keys to achieving goals is understanding the importance of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation is when you engage in an activity because you find it personally satisfying and enjoyable, while extrinsic motivation is when you do something to gain a reward or avoid punishment.
Examples of Intrinsic Motivation
Examples of intrinsic motivation include doing an activity because you find it challenging, enjoyable, or interesting. Reading a book, playing a musical instrument, or learning a new language are all examples of intrinsically motivated activities.
Another example of intrinsic motivation is when an employee fully engages themselves in their work because they find it fulfilling or because they believe in the company’s mission.
Examples of Extrinsic Motivation
Extrinsic motivation comes from external factors such as rewards or consequences. Examples of extrinsic motivation include working long hours to earn a promotion or a bonus, going to the gym to lose weight, or studying for a test to get a good grade.
Another example of extrinsic motivation is when an employee shows up to work on time because they want to avoid getting in trouble or being reprimanded by their supervisor.
Combining Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation
While both types of motivation can be effective in achieving goals, research shows that combining intrinsic and extrinsic motivation can lead to the most success. One way to do this is by finding personal satisfaction in the rewards that come from achieving extrinsic goals.
For example, if you are trying to lose weight for a prize or a competition, you could also focus on how good you feel after exercising and eating healthy. In the workplace, finding intrinsic fulfillment in extrinsically motivated goals can be achieved by showing employees how their work contributes to the overall mission of the company, and how fulfilling their work can be both intrinsically and extrinsically rewarding.

Conclusion
Knowing the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation examples is an important factor in increasing your motivation level. Intrinsic motivation leads to a long-term commitment to a goal and is a more stable form of motivation.
Extrinsic motivation can provide a short-term boost to motivation but can be unstable and dependent on external factors. It is important to find a balance between the two to achieve success and fulfillment.

